 |
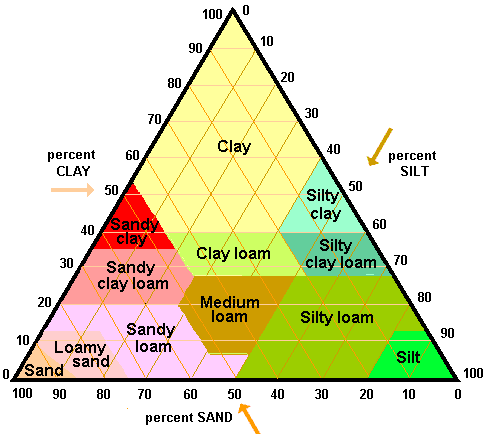
| Soil Triangle |
Shine Test – Roll *moist soil into a ball and rub once or twice against a hard, smooth object such as a knife blade or a thumb nail. A shine on the rubbed surface indicates clay in the soil. The more it shines, the more clay is in the soil.
Ribbon Test – Roll *moist soil into a long thin shape and then squeeze out between the thumb and forefinger to form the longest and thinnest ribbon possible. The longer the ribbon, the more clay is in the soil. Soils with high silt content will tend to flake rather than ribbon.
Feel Test – Rub *moist to wet soil between the thumb and fingers to assess the percentage of sand (sand feels gritty). Silt feels smooth and silky like talcum powder but is not sticky.
Sticky Test – Compress *moist to wet soil between the thumb and forefinger. Note how strongly it adheres to the thumb and forefinger upon release of pressure and how much it stretches. Alternatively, throw it at your partner’s forehead or the truck window. The more it sticks the more clay is in the soil.
Taste Test - A small amount of soil is worked between the front teeth. Sand is distinguished as individual grains which grit sharply against the teeth. Silt particles produce a general fine grittiness, but individual grains cannot be identified. Clay particles have no grittiness.
(* Moist soil feels damp but no visible water is present. A small amount of moisture can be observed on the palm of the hand when a sample is very tightly squeezed and then released. Moist soils can be molded into shapes like potting clay.)
 |
| Soil Texture Key |
Field Manual for Describing Soils 3rd edition
Ontario Institute of Pedology, 1985
Wetland Soils Genesis Hydrology, Landscape Classification”
J.L. Richardson & M.J. Veprakas eds. 2001
Adapted from Thein, S.J. 1979.
A flow diagram for teaching texture
by-feel analysis.
J.Agron.Ed.8:54-55
